What Is Workflow Automation? How It Works, Why You Need It, and How to Measure ROI
Somewhere between the third forwarded email and the second “just circling back,” work starts to feel a little absurd.
A request comes in. It gets copied. Pasted. Re-entered. Forwarded again. Someone updates a spreadsheet. Someone else asks for the latest version. And just like that, half the effort goes into managing the work instead of actually doing it. Not ideal.
This is the invisible drag inside most organizations. In regulated government and enterprise environments, that drag doesn’t just waste time — it introduces risk.
The manual handoffs. The approval bottlenecks. The “Who has this now?” moments that eat up time and patience in equal measure.
Workflow automation exists to smooth that friction out.
At its simplest, it’s software that moves tasks along predefined steps automatically—routing requests, applying rules, triggering notifications, and keeping a clean record of what happened and when. No chasing. Fewer errors. Less guesswork.
It’s not flashy. But it changes everything.
What is Workflow Automation?
At its most practical level, workflow automation is simply this: using software to carry out repeatable steps, rules, and handoffs automatically. Not someday. Not when someone remembers. Immediately—because the system is designed to move the work forward.
Think of a workflow as the invisible choreography behind everyday operations. Something happens. That’s the trigger. A task is created. It’s assigned. Maybe it needs approval. Maybe it branches in two directions. Notifications go out. Deadlines tick in the background. Every action leaves a trace, an audit trail you can look back on later and say, “Yes, this moved from A to B to C, exactly as planned.”
It sounds tidy because, ideally, it is.
A proper workflow usually includes a few essential ingredients:
A trigger that starts the process
Defined tasks or actions
Rules that determine who gets what and when
Approvals or decision points
Automated routing and notifications
A record of activity (timestamps, status updates, history)
Now, just to clear the air—workflow automation is not a glorified to-do list. It’s not a stack of email templates firing off randomly. And it’s not a one-off robotic script clicking buttons in the dark with zero oversight. Without structure, governance, and visibility, that’s not workflow automation. That’s patchwork.
Common workflow triggers include:
A new request submitted (via form, email, or API)
A status change in a record or case
An approaching SLA or date threshold
When those moments occur, the system doesn’t wait for a nudge. It acts. And that shift—from reactive to automatic—is where the real difference begins.
What is Workflow Automation Software?
If workflow automation is the decision logic—the rules, conditions, and handoffs—then workflow automation software is the environment that actually runs it. One is the thinking. The other is the doing.
You can define all the “if this, then that” rules you want in a document or a slide deck. But until those rules live inside a system built to execute them consistently, track them, and secure them, they’re just theory. Helpful theory, maybe—but still theory.
Enterprise-grade workflow automation software provides the framework where that logic operates reliably at scale — with governance, auditability, and secure integrations built in. It typically includes a visual way to design workflows and configure rules, so teams can map out triggers, approvals, and branching paths without relying entirely on custom code. It also supports integrations and APIs, because work rarely stays confined to a single platform. Systems need to exchange data cleanly, and in real time.
Beyond that, mature platforms handle automated notifications, escalations, and scheduled actions—those time-based nudges that prevent tasks from stalling. And just as important, they enforce access control and authentication, ensuring the right users can act, approve, or view information according to defined permissions.
For example, a RESTful API can create, search, or update records while accepting structured JSON data from web forms or third-party systems. That means a request submitted externally can automatically generate or update a record internally—without manual re-entry.
That’s the distinction. Not just automation logic on paper, but a governed system that executes it, securely and consistently.
What is Workflow and Process Automation?
Here’s where people start mixing terms—and honestly, I get it. They sound interchangeable. They’re not. Close cousins, maybe. Not twins.
Workflow automation is about the sequence. The baton pass. Who does what next, and under which conditions. A request comes in, it’s assigned, reviewed, approved (or rejected), and moved forward. Step by step. Almost like a relay race, except no one drops the baton because the system won’t let them. That’s the micro view.
Process automation zooms out.
Now we’re looking at the whole machine: policies, compliance controls, reporting structures, integrations between systems, performance metrics, audit requirements. It’s the end-to-end orchestration of how a service operates—not just the individual tasks, but the guardrails around them. Think less “task routing” and more “operational blueprint.”
If it helps, picture a set of small gears turning inside a much larger mechanism. The inner gear? That’s workflow (micro). The outer housing that keeps everything aligned, measured, and compliant? That’s process (macro). One lives inside the other.
And in real-world environments—especially compliance-heavy industries or multi-team service delivery—you usually need both. Routing tasks without governance is chaos with better lighting. Designing policy without automated execution is theory that nobody follows consistently.
Together, though? That’s where things start humming. Not perfectly. But close enough that you stop firefighting and start steering.
How Does Workflow Automation Work?
It’s less magic than people think. More choreography.
When someone asks, how does workflow automation work? the honest answer is: it follows a lifecycle. A rhythm. Work comes in, the system evaluates it, moves it, nudges the right people, and keeps score in the background. Rinse and repeat—though “repeat” makes it sound dull, and it’s actually pretty elegant when done right.
Let’s break the lifecycle into five structured stages.
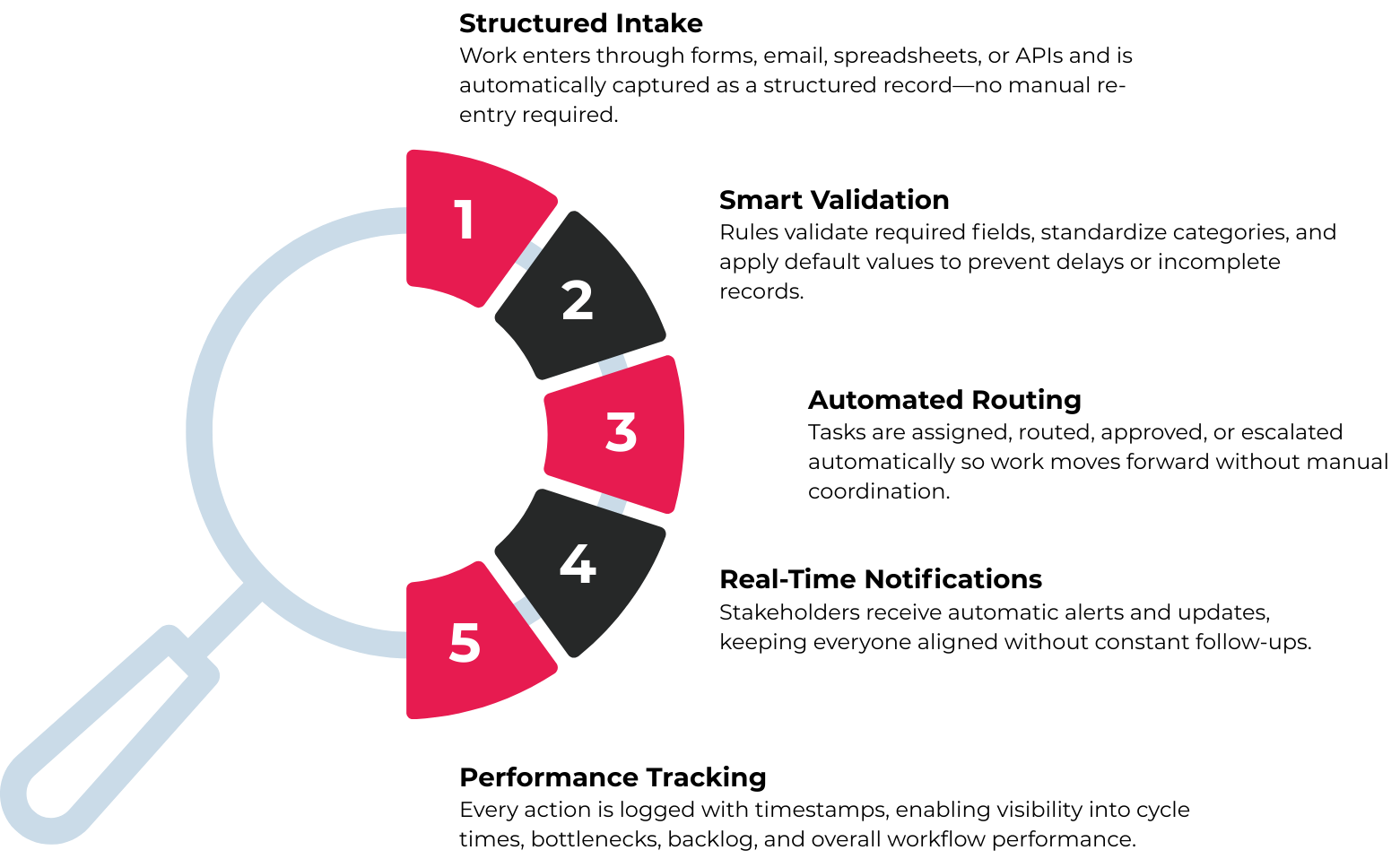
Step 1 — Capture the Work (Intake)
Everything starts with intake. That first spark.
Maybe it’s an email. Maybe a web form. Sometimes it’s a spreadsheet upload—yes, CSV files still haunt us—or an API call from another system. The point is, the request lands somewhere structured instead of floating around in someone’s inbox.
For example, a RESTful API can be called from internal or external web forms and other systems, with data mapped and imported automatically to create or update records. No retyping. No copy-paste gymnastics. The system simply receives the information and spins up the appropriate record behind the scenes.
Clean start. Or at least cleaner.
Step 2 — Apply Rules and Defaults
Once the work exists inside the system, logic kicks in.
Required fields get validated. Categories are standardized. If someone forgets to include a priority level—or leaves a field blank—the system can apply predefined default values. That way, the record doesn’t stall just because someone was in a rush (we’ve all been there).
This is where consistency begins to replace guesswork.
Step 3 — Orchestrate Tasks and Handoffs
Now the baton starts moving.
The system routes the task to the appropriate queue or individual. It assigns owners. It triggers approval steps if needed. If a deadline slips, escalation rules can quietly elevate the issue without anyone having to remember to do it manually.
Instead of “Who has this?” the answer is visible. Structured. Tracked.
Step 4 — Notify and Synchronize
Of course, work doesn’t happen in isolation.
Notifications go out to staff or stakeholders when records are created or updated. Automatic email alerts can be generated for new items, status changes, or required actions. The system becomes the gentle tap on the shoulder—sometimes a firm tap—keeping momentum intact.
No endless follow-ups. Fewer surprises.
Step 5 — Track Outcomes
And finally, the part most teams forget until audit season: tracking.
Every status change is timestamped. Every action leaves a trail. You can measure cycle time, monitor backlog, analyze bottlenecks. Over time, patterns emerge—where things slow down, where approvals pile up, where resources might be stretched thin.
That visibility? It’s the quiet superpower of workflow automation.
So while the mechanics are straightforward—capture, validate, route, notify, track—the impact compounds. Slowly at first. Then all at once.
See What Your Processes Are Really Costing You—and Calculate the Measurable ROI of Workflow Automation
How Does Workflow Automation Help You?
Here’s the part that actually matters. Not the diagrams. Not the terminology. The impact.
Speed, for starters. When handoffs are automated instead of manually forwarded, work moves. No waiting for someone to notice an email. No “I thought you had it.” Fewer bottlenecks. Cycle times shrink—not overnight, maybe, but steadily. And that steady improvement adds up faster than most teams expect.
Then there’s consistency. The system validates required fields. It applies standard categories. It enforces the same steps every single time. That means fewer missing details, fewer awkward follow-ups, fewer rework loops. The output becomes predictable in a good way. Boring, even. Boring is underrated.
Capacity shifts too.
When staff aren’t spending their mornings rekeying information or chasing approvals, they can focus on judgment calls, analysis, stakeholder communication—the work that actually requires a brain. I’ve seen teams realize, almost sheepishly, that they didn’t need more headcount. They just needed fewer manual steps. Not always, but often.
Visibility is another quiet win. Real-time status tracking replaces those “Where is this at?” emails that clog inboxes and fray patience. Anyone with permission can see progress, timestamps, backlog levels. The guesswork fades.
And in compliance-heavy environments, the benefits get even sharper. Consistent record handling. Documented approvals. Retention applied properly. An audit trail that exists without a last-minute scramble.
In one pilot focused on executive correspondence intake, automation reduced manual intake effort by hundreds of hours over a three-month period while managing more than 5,000 correspondences annually. That’s not theoretical. That’s reclaimed time.
So how does workflow automation help you? It removes drag. It creates clarity. And—quietly—it gives teams their focus back.
Why Do We Need Workflow Automation?
Because volume creeps up. Complexity multiplies. And humans, last I checked, don’t scale infinitely.
Most organizations don’t run one clean, linear workflow. They run dozens—variants, exceptions, special cases. In one pilot environment, more than 20 different workflows fed into a single intake stream. Twenty-plus. That’s not a process; that’s controlled chaos wearing a name badge. Without structure, intake alone becomes a maze of tribal knowledge and “ask Sarah, she knows.”
As volume and variation increase, so does risk.
Manual steps invite manual errors. Fields get skipped. Approvals are forgotten. Deadlines slide by quietly. No one intends for it to happen, but it does—especially when teams are juggling competing priorities. Workflow automation reduces that exposure by enforcing the steps that must occur. It doesn’t rely on memory or good intentions.
There’s also the matter of standardization. When workflows are codified inside a system, teams operate from the same playbook. Not five interpretations of it. That consistency makes onboarding faster, too. New hires don’t have to decode unwritten rules; the system guides them through how work actually gets done.
And then there’s the service experience. Predictable timelines. Clear status updates. Fewer black holes where requests disappear.
Why do we need workflow automation? Because scale without structure eventually breaks something. Automation adds the structure before that breaking point arrives.
What Are Workflow Automation Tools?
The short answer? There isn’t just one category.
When people ask, what are workflow automation tools? they’re usually picturing a single platform that “does automation.” In reality, the ecosystem is broader—and a little messier—than that. Different tools tackle different layers of the problem.
Common Categories
At the center are workflow or BPM (Business Process Management) platforms. These are purpose-built systems for designing, executing, and monitoring structured workflows. They handle routing, approvals, rules, and reporting—the backbone of automation.
Then you have ticketing or case management systems, often used in IT, HR, or service environments. These tools track requests as structured records and move them through defined stages. Not all are deeply configurable, but many support workflow logic.
Behind the scenes, integration platforms (iPaaS) connect systems together. They move data between applications—CRM to ERP, web form to database—so workflows don’t stall inside silos.
There’s also RPA (robotic process automation), which automates repetitive desktop tasks by mimicking human clicks and keystrokes. Useful, though typically narrower in scope and sometimes fragile if underlying interfaces change.
Don’t overlook document and records management tools, which enforce retention, control access, and maintain audit trails. In compliance-heavy sectors, that’s not optional—it’s foundational.
And increasingly, AI-assisted tools support classification, drafting, summarization, or routing decisions. They don’t replace workflow logic, but they enhance it.
Examples Within the ccmEnterprise Suite
Within the ccmEnterprise Suite, workflow automation is supported through several building blocks rather than a single monolithic feature.
For instance, a RESTful API enables external or internal systems to create, search, and update records, and attach files using structured JSON submissions. That allows web forms or third-party platforms to initiate workflows automatically.
The suite also supports automated intake and processing—generating records and triggering workflow initiation without manual intervention. And where cross-organization collaboration is required, tools like ccmExchange enable the secure exchange of records and attachments between organizations.
These are examples, not a one-size-fits-all prescription. The right mix depends on the complexity, risk profile, and integration needs of the environment.
How to Measure ROI for Workflow Automation
Here’s where the conversation shifts from “this sounds useful” to “show me the numbers.”
Measuring ROI for workflow automation isn’t complicated—but it does require a bit of honesty about how things work today. Not how we think they work. How they actually work on a Tuesday afternoon when three requests land at once and someone’s out sick.
Here’s how to structure that measurement.
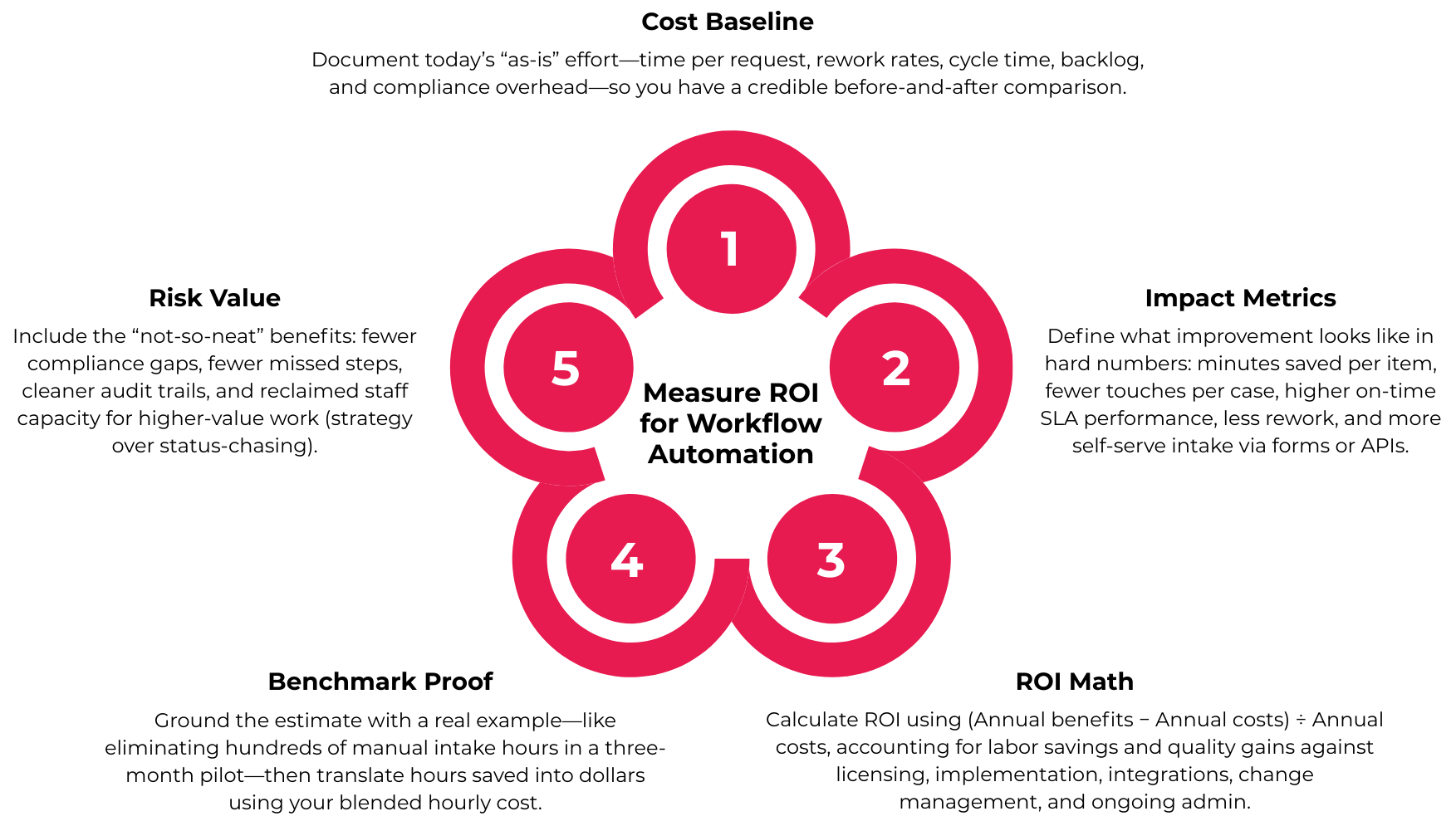
Step 1 — Baseline Current Costs
Start by capturing your current reality.
How much time does one transaction really take? Intake, triage, data entry, routing, follow-ups—add it up. Ten minutes here, eight minutes there. It accumulates faster than most teams expect.
Look at error and rework rates. How often are submissions incomplete? How many items get bounced back for clarification? That’s labor, too.
Measure cycle time and backlog. How long does a request sit before completion? How many are open at any given moment?
And don’t forget compliance-related costs: record retrieval, audit preparation, documentation clean-up. Those “once a year” scrambles have a price tag.
This baseline is your starting line.
Step 2 — Define Measurable Post-Launch Metrics
After automation is in place, track tangible improvements.
Calculate minutes saved per item and multiply by monthly volume. If you save six minutes per request and process 3,000 per month, that’s 18,000 minutes—300 hours—reclaimed. Per month.
Measure fewer touches per case. Fewer status checks. Fewer manual handoffs.
Track SLA improvements. Did on-time completion increase from 82% to 96%? That’s not cosmetic—that’s service quality.
Monitor rework reduction. And consider deflection: how many submissions now arrive via structured forms or APIs instead of manual handling?
Numbers tell the story. If you let them.
Step 3 — Apply the ROI Formula
The formula itself is straightforward:
(Annual benefits − Annual costs) ÷ Annual costs
Benefits include labor savings, reduced rework, and potentially avoided compliance penalties. In structured environments, this may also include security reviews, infrastructure validation, and integration governance. Be thorough. Be realistic. Slightly conservative estimates are usually wiser than optimistic ones.
Step 4 — Use a Benchmark Example
In one pilot focused on executive correspondence intake, automation eliminated hundreds of hours of manual intake effort over a three-month period.
Run the math. If 300 hours were saved and the blended hourly cost is $45, that’s $13,500 in labor savings in one quarter alone. Annualized, the impact grows quickly.
Step 5 — Don’t Ignore Risk and Compliance Value
Not every benefit fits neatly in a spreadsheet.
Standardized outputs reduce incomplete records. Consistent workflows lower the chance of missed approvals. Audit trails exist automatically, not retroactively.
And perhaps most valuable—though harder to quantify—staff capacity shifts toward higher-value work. Strategy instead of status checks. Analysis instead of administration.
That, too, is ROI.
Bringing It All Together
So—what is workflow automation?
At its core, it’s software-driven execution of repeatable steps, rules, and handoffs. It captures work, applies logic, routes tasks, notifies stakeholders, and tracks outcomes without relying on memory or manual nudges. That’s the mechanics.
The impact is bigger.
Done well, workflow automation speeds up cycle times, standardizes outputs, reduces errors, increases visibility, and strengthens compliance. It shifts staff effort away from administrative busywork and toward higher-value decisions. And when measured properly—through time saved, reduced rework, SLA improvements, and risk reduction—the ROI becomes tangible, not theoretical.
The tools vary. The structure doesn’t.
If you’re considering workflow automation, start small. Map one high-volume process. Measure it honestly. In high-volume correspondence, case management, or compliance-driven environments, that first mapped process often reveals more friction than expected.
Ready to see what that could look like in your environment? Let’s talk.


